Economic Overview
Global Review
Global economic activity in 2015 remained largely subdued.
Global growth is projected at 3.4% in 2016 and 3.6% in 2017.
Gradual slowdown and rebalancing of economic activity
in China, lower prices for energy and other commodities,
and gradual tightening of monetary policy in United States
influenced the global outlook. Growth in emerging and
developing economies contributed to 70% of global growth
in 2015.
Economic adjustments on the back of global slowdown will
have material impact on economic recovery. While deflation
and revitalisation of European Union and Japan has led to
central banks undergoing quantitative easing programmes,
United States is looking at rate hikes this year on the back
of strengthening economy and wage escalations. Some
improved data releases like firming of oil prices, support by
major central banks, and lower capital outflows from China
are resulting in improved investor sentiments.
GDP Growth Trend (%)

Key Snapshot
- The US economy grew by 2.4% in CY 2015, just as
it did in CY 2014. The challenges were weaker than
expected domestic demand, lacklustre performance
of the manufacturing sector, declining exports due to
stronger dollar and adverse external trade environment.
- The Euro Area as a whole grew by 1.6% in CY 2015,
faster than CY 2014. The economy received robust
support from three tailwinds: a) lower oil prices
(bolstering consumer expenditure / domestic demand);
b) expansionary fiscal policies; and c) an accommodative
ECB. The challenges, however, were: sub-zero inflation,
high non-performing loans and debt trajectories, low
investment and eroding skills of the working population
due to long-term high unemployment in the region.
- Economic growth for China was 6.9% in CY 2015. The
slowdown and rebalancing of the economy led to a
decline in investment in real estate, manufacturing and
allied industries.
- The economic performance of many African economies
was lower than expectations. Resource-rich countries in
Africa suffered owing to a decline in commodity prices
and also because their frontier markets were adversely
affected by tighter global financing conditions.
Indian Economy
India’s economic growth for 2015-16 was 7.6%, overtaking
its formidable economic rival China (Source: CSO). The
decline in oil price, while affecting large parts of the world,
has helped the economy lower its huge import bill. The
Government of India has also ushered in a series of reforms
in agriculture, manufacturing, infrastructure and services
sectors to bolster economic performance and make growth
more inclusive. Declining fiscal deficit, moderating inflation
and a comfortable interest rate trajectory were definite
positives as well. India stands out as one of the rising stars in
a world characterised by volatility and financial turbulence on
account of its economic stability, favourable demographics,
proactive Central Bank and a Government focused on
consistent reforms.
Key Snapshot
- The Union Budget 2016-17 focused on enhancing
farm output and welfare of farmers.
- Consistent fiscal consolidation has reduced
Government’s fiscal deficit to close to 4% of GDP (on
a 12-month rolling basis), down from a peak of 7.6% in
2009.
- The Government’s Make in India initiative has been
a resounding success. It has encouraged domestic
entrepreneurship and even attracted FDI to the country
significantly. In the period of 17 months (October 2014
to February 2016) after the launch of Make in India,
FDI inflows increased by 37% (Source: Ministry of
Commerce and Industry).
- Digital India will have a transformational impact on
Indian society. It represents a connected society, where
every citizen will be connected to the internet. This will
help enhance education, employment, efficiencies,
governance and controls.
- Internet penetration is around 30% in India; and is
projected to touch around 35% next year (Source:
IAMAI).
- The Government’s Smart Cities Mission is a revolutionary
concept in terms of overall infrastructure, sustainable
real estate, communications and market viability. There
are many technological platforms involved, including
but not limited to automated sensor networks and data
centres
African Economy
Africa’s economy as a whole remained more resilient
to global volatilities, compared to many other emerging
and developing regions. The continent’s growth enablers
comprise: the vastly improved macroeconomic environment,
benefiting businesses; reduction of external debt and social
conflicts; improved political and economic governance;
growing domestic demand; buoyant services sector; financial
services growth in line with an upswing in information and
communications technology; and rapid internet penetration.
Poverty in the continent is also seeing a declining trend.
Africa’s young and aspirational population is acting as
an agent of change in largely conservative societies. The
continent’s youth bulge will drive the next era of growth and
transformation.
Key Snapshot
- A large African middle-class is emerging, over
350 Mn people, driving the culture of innovation and
policymaking.
- Africa is the world’s second fastest growing FDI
destination, just behind Asia Pacific.
- Sustainable policies for urbanisation, manufacturing
growth, agricultural output, along with education and
empowerment can act as key catalysts.
- Less focus on oil exports and other commodities will
augur well for the economy, going forward.
South Asian Economies
Bangladesh shows significant potential in South Asia. It
has a stable democracy with focus on empowerment from
grassroots. The economy’s key growth enablers comprise:
growing manufacturing and construction sector, robust
service sector and higher private consumption bolstered
by remittances. These pivots have resulted in sustainable
economic growth for the nation.
Sri Lanka is also a stable, democratic society with focus on
inclusive growth. The island nation’s economic potential
is considerable. The country has a strong base of human
capital and reliable infrastructure. It also occupies a strategic
position in Asia, the fastest growing region in the world; and
investments over the last decade (especially in ports and
other transport-related facilities) can take advantage of this
opportunity.
Key Snapshot
- Bangladesh’s GDP grew by 6.6% in 2015 vis-à-vis 6.1%
in 2014.
- Growth is expected to further inch up to 6.7% in 2016,
led by strong garments exports and rising private
consumption as government employees get wage
increase.
- Real GDP growth for Sri Lanka was 4.8% in 2015
(broadly unchanged from 2014), driven by robust
growth in services and agriculture, as well as a positive
contribution from manufacturing.
- Sri Lanka’s economy is expected to grow by 5.3%
and 5.8% in 2016 and 2017, respectively on back of
strong domestic demand, and higher private and public
investments.
Megatrends that drive the Company’s business
- Internet users in India have risen from 50 Mn in 2007 to
100 Mn in 2010; and more than 300 Mn in 2015. Of the
306 Mn internet users as on December 2015, 219 Mn
users are from urban India. The urban user base grew
by 71% year-on-year. On the other hand, the rural user
base went up by 93% from December 2014 to reach
87 Mn at the end of December 2015.
- India is a lucrative market for global and domestic
smartphone manufacturers. Smartphone shipments
increased by 55% between 2014 and 2015 (Source –
IDC). The country has an established base of 184 Mn
users. Enhanced focus on manufacturing affordable
handsets with indigenous technology will further spur
mobile telephony.
- With rise in affordable smartphones and more users
preferring 3G / 4G, data usage is likely to grow by 12
times from 2015 to 2020. Mobile data traffic increased
by 89% between 2014 and 2015; and mobile data
traffic grew by 2.4 times faster than India’s fixed IP traffic
(Source: Cisco VNI forecasts). Network migration from
2G to 3G / 4G is driving a change in data consumption
from low bandwidth to high-bandwidth applications,
along with more availability of relevant content.
- India is in a sweet spot to leverage market opportunities
emerging through Internet of Things (IoT). A strong
ecosystem of IT organisations, renewed focus on
manufacturing, significant opportunities in education,
healthcare and agriculture; and enormous growth
in mobile internet usage will act as key catalysts in
supporting investments in IoT. The Government of
India’s initiative of smart cities requires seamless digital
and physical infrastructure to be shared efficiently
across devices and applications; IoT will play a critical
role in fulfilling this vision.
- Convergence is a global trend for the telecom
business of the future. It enables a user to have a
uniform experience, both at home and on the move.
Combination of conveniences, freedom of movement,
and personalised services, along with high quality and
speed of fixed communications will enable a seamless
network experience for the end user.
- India is on the cusp of a huge digital revolution. Digital
Literacy Mission will touch 60 Mn rural households as
per the Union Budget of India 2016. The Government of
India also plans to connect 550 farmer markets in the
country through the use of technology. The Digital India
drive will bring along a transformative impact on every
citizen through the medium of internet.
- The proposed policy environment through M&A rules,
spectrum sharing guidelines and 20-year spectrum
positions for telecom operators not only enhances
business certainty, but also encourages industry
consolidation and healthy growth. The gains in network
efficiency that sharing can provide will benefit operators
and customers alike. Upcoming auctions will further
help in building stronger networks.
- Mobile banking is on a rise in India and Africa. India’s
largest wallet company has around 120 Mn wallets
with other companies estimated to have 30 Mn+. This
is significantly more than the number of credit cards in
India. Additionally, mobile phone banking technology
is bringing more people in Sub-Saharan Africa into the
formal financial sector and the economy more broadly.
- Africa, with a median population of less than 20
years, is on the cusp of a mobile data revolution as
3G and 4G deployments gather scale with more
affordable handsets available. Mobile data is helping
people elevate their lives with a large proportion of
the population relying on the internet for education,
financial transactions, healthcare, and so on.
- E-commerce is at the epicentre of Africa’s thriving
economy. The continent’s digital evolution is a promising
prospect with the e-commerce market expected to be
worth approximately USD 50 Bn by 2018. India has
an exciting ecommerce story as well, with online retail
growing 4.5x in the last three years. India’s e-commerce
industry is likely to be worth USD 38 Bn by 2016, a 67%
surge over the USD 23 Bn revenues for 2015 (Source:
Deloitte).
Industry Overview
Indian Telecom Sector
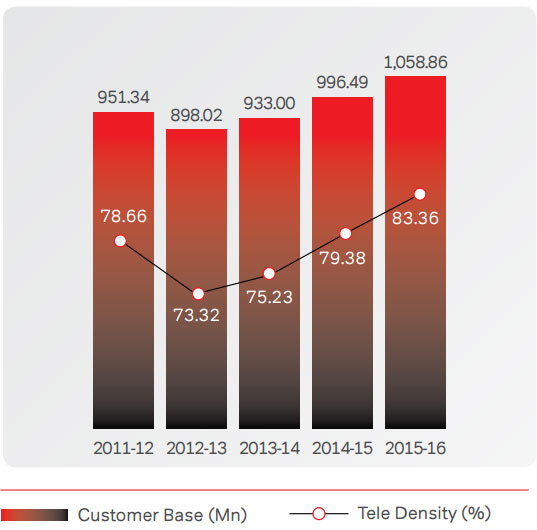
India’s total customer base stood at 1058.86 Mn with a teledensity
of 83.36%, as on March 31, 2016, having grown from
a base of 996.49 Mn and tele-density of 79.38% last year.
The urban tele-density stood at 154.01%, whereas the rural
tele-density stood at 51.37%, as on March 31, 2016. India’s
telecom market is witnessing a strong growth of internet
users; and now has the world’s second highest number of
internet users. The wire-line customer base is 25.22 Mn at
the end of March 31, 2016 vis-à-vis 26.59 Mn at the end of
March 31, 2015.
Among the service areas excluding metros, Himachal
Pradesh has the highest tele-density (127.41%) followed
by Tamil Nadu (118.12%), Punjab (106.09%), Kerala
(102.27%), Karnataka (101.88%), Gujarat (100.05%) and
Maharashtra (98.98%). Among the three metros, Delhi tops
with 236.30% tele-density. On the other hand, the service
areas, such as Bihar (54.31%), Assam (57.55%), Madhya
Pradesh (64.18%), Uttar Pradesh (65.83%) and Odisha
(69.09%) have comparatively low tele-density.
Rural penetration (low at nearly 50%) represents huge
headroom for growth. With urban tele-density crossing
150%, internet penetration and experience will be the key
drivers of growth in urban areas. With the government’s
favourable regulation and policies and the developing 4G
ecosystem, India’s telecommunication sector is expected to
witness an explosive data growth in the next few years.
Tele Density: India (%)
During the year, the Company introduced a comprehensive
network transformation programme - Project Leap aimed
at delivering a world class network. This programme will
see an investment of ` 600,000 Mn in the next three years.
The programme will help Airtel build a smart and dynamic
network that will significantly improve the quality of both
voice and data services across India. The programme aims
to deliver a truly differentiated customer experience and
reinforce its commitment to build a future-ready network.
Airtel has acquired rights to use 2x5 MHz spectrum in
the 1800 MHz Band from Videocon Telecommunications
Limited (VTL) which was allotted to VTL by the Department
of Telecommunication (DoT) on April 05, 2013 for six
circles, namely, Bihar, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, UP (East),
UP (West) and Gujarat at an aggregate consideration of
` 44,280 Mn.
Bharti Airtel Limited and its subsidiary, Bharti Hexacom
Limited entered into definitive agreements with Aircel
Limited and its subsidiaries Dishnet Wireless Limited and
Aircel Cellular Limited to acquire rights to use 20 MHz 2300
Band 4G TD spectrum for eight circles namely, Tamil Nadu
(including Chennai), Bihar, Jammu & Kashmir, West Bengal,
Assam, North East, Andhra Pradesh; and Odisha at an
aggregate consideration of ` 35,000 Mn. The closing of the
said transaction is subject to certain customary regulatory
approvals and other closing conditions.
During the year, the Company had launched 3G services
in its gap circles and the high-speed 4G services were also
commercially launched across India.
With the proposed spectrum acquisitions from Videocon
and Aircel, the Company is set to become a pan-India 4G
operator.
African Telecom Sector
Africa is among the fastest growing regions, but had faced
significant headwinds in the last year as a result of global
trends and region specific issues. The global commodity
super-cycle has come to an end, sharply lowering the price of
oil, gas, metals and minerals. As a net commodities exporter,
Africa is deeply affected by falling commodity prices, putting
pressure on the current account and fiscal balances.
The revenue-weighted currency depreciation vis-à-vis the US
Dollar across 17 countries in Africa over the last 12 months
(exit March 31 rates) has been 5.7%, primarily caused by
depreciation in Malawi Kwacha by 54.9%, Zambian Kwacha
by 45.1% and Tanzanian Shilling by 17.3%. In terms of
the 12-month average rates, the revenue-weighted Y-o-Y
currency depreciation has been 18.3%, mainly caused by
depreciation in Zambian Kwacha by 51.8%, Malawi Kwacha
by 32.1%, Ugandan Shilling by 25.1%, Nigerian Naira by
18.0% and CFA by 14.2%.
However, Africa’s market with a billion-plus population
promises considerable opportunities for African telecom
sector. Data and mobile money have a significant potential
for sustained growth; and with increasing adoption of
smartphones this trend is set to continue.
Development in Regulations
The year saw several regulatory changes and developments.
The significant regulatory changes were:
India
- Sharing of Active Infrastructure: In February 2016, the
Department of Telecommunications issued Guidelines
for Sharing of Active Infrastructure among service
providers, based on mutual agreements. As per the
guidelines, active infrastructure sharing will be limited
to antenna, feeder cable, Node B, Radio Access Network
(RAN) and transmission system only.
- Valuation and Reserve Price of Spectrum: In January
2016, TRAI issued its recommendation on Valuation
and Reserve price of Spectrum in 700 MHz, 800 MHz,
900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz, 2300 MHz and 2500
MHz Bands. As per the recommendation, auction in all
the bands should be conducted simultaneously. DoT
should carry out carrier re-assignment exercise in the
800 MHz band at the earliest; and ensure that the entire
spectrum that is available for commercial use is put to
auction and it should be in contiguous blocks. Spectrum
in 700 MHz band should be offered in the block size of 5
MHz (paired). In case a TSP is able to win more than one
block of spectrum in the upcoming auctions, it should be
allocated spectrum in contiguous blocks.
- Liberalisation of Spectrum: On November 05, 2015,
the Department of Telecommunications issued the
Guidelines on Liberalisation of Administratively allotted
spectrum in 800 MHz and 1800 MHz band in a service
area for the balance validity period of right to use of
spectrum, after payment of auction determined price,
prorated for the balance validity period. The entry fee
paid will be pro-rated for the balance validity period of
the right to use spectrum; and will be deducted from the
total amount to be paid by the TSP for liberalising the
spectrum. In case the spectrum gets liberalised, the One
Time Spectrum Charges (OTSC) will be charged and the
same has to be paid by the licensee.
- DoT guidelines on Spectrum Trading: In October 2015,
the DoT issued the guidelines on Spectrum Trading.
Spectrum Trading shall be allowed between two access
service providers, holding Cellular Mobile Telephone
Service (CMTS) / Unified Access Service License (UASL)
/ Unified License (Access Services) (UL(AS)) / Unified
License (UL) with authorisation of Access service in
a licensed service area. All access spectrum bands
earmarked for Access Services by the Licensor will be
treated as tradable spectrum bands. Only that spectrum
can be traded that has been assigned through an auction
in 2010 or afterwards, or on which TSP has already paid
the prescribed market price.
- TRAI releases Telecom Consumers Protection (Ninth
Amendment) Regulations, 2015 on Call Drop: On
October 16, 2015 TRAI releases Telecom Consumers
Protection (Ninth Amendment) Regulations, 2015 on Call
Drop, which mandates the originating service provider
providing Cellular Mobile Telephone Service, for each call
drop within its own network compensate the consumer
by crediting the account of the calling consumer by
1 rupee subject to a maximum of 3 dropped calls in a
day; and inform the consumer within four hours of the
occurrence of a call drop. The Supreme Court ruled in
favour of Telco’s where it struck down TRAI’s directive.
- Spectrum Sharing: On September 24, 2015 the
Department of Telecommunications issued the
guidelines on Spectrum Sharing. Spectrum sharing will
be allowed only for the access service providers holding
CMTS license, UASL, UL (AS) and UL with authorisation
of Access Service in a Licensed Service Area (LSA),
where both the licensees are having spectrum in the
same band. Both the licensees shall ensure that they
fulfill the specified roll-out obligations and specified
Quality of Service norms.
- TRAI’s recommendations on ‘Introducing Virtual
Network Operators in Telecom Sector’: In May 2015,
TRAI made its recommendations on Introducing Virtual
Network Operators in telecom sector to DoT. Virtual
Network Operators (VNO) to be introduced through a
proper licensing framework. The terms and conditions of
sharing of infrastructure between the Network Services
Operator (NSO) and VNO should be left to the market i.e.
on the basis of mutually accepted terms and conditions
between the NSO and the VNO. An NSO shall allocate
a numbering range to their VNO(s) from the numbering
range allocated to it by the licensor. VNOs shall also
utilise the LRN and network codes of the parent NSO for
the purpose of routing of calls.
Africa
- Zambia, Tanzania, Malawi and Other SADC
Countries: The Governments within the SADC region
have commenced bilateral arrangements to implement
the Roam Like at Home tariffs imposed by the SADC
governments.
- Burkina Faso and Congo B: The Regulator has
performed a cost study to determine the interconnect
rates that will be applicable in 2016. Basis that, the
Regulator has kept the rates unchanged.
- Rwanda: The interconnect rates glide path, which had
been set by the Regulator has come to the end of the
term. Operators are now awaiting new rates from the
Regulator.
- Uganda: The Regulator has indicated that it will review
the interconnect rates; and is in the process of recruiting
a consultant to handle the process.
- Burkina Faso: The Regulator is proposing the introduction
of a tax on incoming international traffic. The industry is
in discussion with the Regulator on this matter. So far no
decision has been taken for its implementation.
- Tanzania: The Government of Tanzania in October 2015
had passed a new regulation that requires Telco’s to list
on the Dar es Salaam Stock Exchange within 12 months,
failing which they have to make a contribution of 0.6% of
its annual gross revenues to the ICT development fund.
- Uganda, Kenya and Rwanda: The Governments in
these three countries are pushing forward the agenda
of the One Area Network. In the last quarter these
Governments have proposed to expand the scope of
services under the regulated tariff to SMS and Data.
- Nigeria: Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC)
has released the Information Memorandum for 2.6
GHz spectrum auction for LTE and has also shared the
consultation paper on Procedures and Guidelines for the
provision of Value Added Services in Nigeria.
- Ghana: The Regulator has proposed to license frequency
in the 800 MHz band. This comes with an obligation for
local shareholding of up to 40%. Consultations between
the industry and the Regulator have taken place and the
final decision is awaited.
- Zambia: The Regulator is proposing to introduce a
unified licensing regime. If this proposal is adopted, it
will affect the existing rights and obligations under the
current licensing. It will also affect our spectrum holding
and introduce new acquisition costs.
- Kenya: The Regulator has agreed to make available to
Airtel at least 10 MHz of the available 800 MHz spectrum
for LTE. The price for the same is under discussion with
the Regulator.
- Niger: The Government has put in place a new law
proposing the introduction of an exclusive international
gateway, which is in violation of the mobile operators’
license.
- DRC: There is a proposed new law that will if passed;
affect the terms and conditions of the license. Some of
the proposals include restrictions on license ownership,
nationalisation of infrastructure and tariff control.
Industry is in discussion with the Regulator to review the
proposed law.
- Malawi: There is a requirement in the license that
the Company should have a minimum of 20% local
shareholding. Airtel has received a written extension of
the 20% local shareholding obligation for another 1.5
years from February 2016.
SCOT Analysis
Strengths
- Spectrum: Strong and expanding network
– Pan India 4G spectrum and 3G spectrum
in 21 circles. Wide spectrum presence with
21.1% spectrum market share (post deals
with Videocon and Aircel); 4G and 3G carrier
aggregation available in 12 and 8 circles,
respectively.
- Presence: #1 telecom player in India and #3
worldwide. The Company is present in 20
countries across South Asia and Africa.
- Scale: The Company’s revenue market share
is the highest in the industry. It also has the
highest subscriber market share with the
largest net additions this year.
- Diversified Portfolio: Vast product line, which
includes telecom services like DTH, Telemedia,
Airtel Business and Tower Infrastructure. The
portfolio also includes other bundled services
like Wynk music, movies, and mobile wallet.
Challenges
- Operations: Geographically varied presence,
integrating operations across India, South Asia
and Africa leveraging common platform.
- Customer Needs: Understanding changing
customer expectations and perceptions in a
fast evolving multi-cultural, multi-lingual, and
multi-technological environment.
- Technological: Harmonisation of multi-band
sub 5MHz of spectrum.
Opportunities
- Data Usage: Data explosion is at its cusp with
the proliferation of affordable smartphones.
Data uptake has also increased with usage
moving from low to high bandwidth content.
- Convergence: Newer and converged needs
across technologies and services targeted to
specific customer segments.
- Internet Space: Significant opportunities
thrown up by the internet across payment
mechanisms, e-commerce, m-commerce
and IoT.
- Investments: Large residual opportunity with
bulk investments in place. Best pan-India
spectrum assets with prime spectrum to yield
data uptake, largest optical fibre network
amongst private players.
Threats
- Competition: Competitor launches and its
impact on the overall industry structure and
profitability, especially data rates across
4G + 3G.
- OTT: Cannibalisation of traditional voice
and messaging – further aggravated by OTT
applications gaining scale.
- Regulatory: Political and economic
uncertainties in Africa and India due to
changes in policies.
- Currency Exposures: Volatility in currencies
due to global macro-economic uncertainties.
Financial Review
Consolidated Figures

Standalone Figures

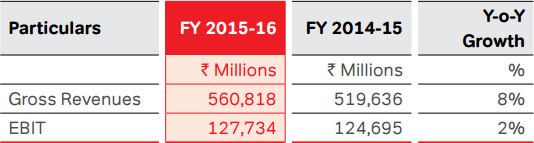
The Company’s consolidated revenues grew by 4.9% to
` 965,321 Mn for the year ended March 31, 2016 (growth of
6.9% after normalising for impact of IUC in India and impact
of divestment of tower assets in Africa). The revenues for
India and South Asia (` 723,881 Mn for the year ended
March 31, 2016) represented a growth of 9.6% compared to
that of previous year (growth of 12.2% after normalising for
impact of IUC in India). The revenues for Africa, in constant
currency terms, grew by 3.1% (growth of 4.2% adjusting for
the impact of divestment of tower assets).
The Company incurred operating expenditure (excluding
access charges, cost of goods sold, license fees and CSR
costs) of ` 413,886 Mn representing an increase of 2.9%
over the previous year. Consolidated EBITDA at ` 341,902
Mn grew by 8.7% over the previous year. The Company’s
EBITDA margin for the full year touched 35.4% vis-à-vis
34.2% in the previous year, primarily due to tighter opex
controls (after adjusting for the impact in reduction of
termination rates, EBITDA margin for the previous year was
34.6%). Depreciation and amortisation costs for the year
were higher by 12.4% to ` 174,498 Mn primarily on account
of spectrum related amortisation cost in India. Consequently,
EBIT at ` 166,434 Mn increased by 5.0%, resulting in a
flat margin of 17.2% vis-à-vis the previous year. The cash
profits from operations (before derivative and exchange
fluctuations) for the year ended March 31, 2016 stood at
` 289,152 Mn vis-à-vis ` 285,280 Mn in the previous year.
Net finance costs at ` 68,866 Mn were significantly higher
by ` 20,403 Mn, compared to that of previous year, primarily
on account of higher interest on borrowings due to spectrum
borrowing cost, higher interest on finance lease obligation
and lower investment income. The Forex and derivative
losses were lower at ` 18,108 Mn (PY: ` 21,530 Mn).
Consequently, the consolidated profit before taxes and
exceptional items at ` 106,200 Mn has declined by 8.2%
over the previous year.
The consolidated income tax expense (before the impact on
exceptional items) for the full year ending March 31, 2016
was almost flat at ` 53,180 Mn, compared to ` 52,928
Mn for the previous year. The effective tax rate in India for
the full year came in at 30.2% (28.8% excluding dividend
distribution tax) compared to 26.5% (25.5% excluding the
impact of dividend distribution tax) for the full year ended
March 31, 2015. The increase in the underlying effective tax
rate in India is primarily on account of expiry / reduction of
tax holiday benefits in select units. The tax charge in Africa
for the full year at USD 189 Mn (PY: USD 203 Mn) has been
lower, primarily due to change in profit mix of the countries.
Exceptional items during the year accounted for net gains
of ` 7,097 Mn. These included impact of gains / losses
on divestment of telecom towers, settlement of various
disputes, few restructuring and integration activities and
revisiting certain accounting positions. After accounting for
exceptional items, the resultant consolidated net income
for the year ended March 31, 2016 touched ` 54,842 Mn,
a 5.8% escalation over the previous year. Net income before
exceptional items for the full year touched ` 47,745 Mn, a
21.5% decline over the previous year.
The capital expenditure for the full year was ` 205,919 Mn
(USD 3.1 Bn), an increase of 10.3%, vis-à-vis the previous
year. Consolidated operating free cash flow for the year
reflected an increase of 6.4% to ` 135,982 Mn.
During the year, the Group has designated the USD
denominated finance lease obligations (‘FLO‘) resulting from
the sale and lease back of telecom tower assets in Africa,
as a hedge against the net investments in subsidiaries with
USD functional currency. The effective portion of the foreign
exchange movements on the hedging instrument has been
recognised in other comprehensive income, so as to offset
the foreign exchange movement on the net investments
being hedged. Accordingly, during the year, foreign exchange
loss of ` 708 Mn (net of tax and non-controlling interests)
has been recognised in other comprehensive income.
Liquidity and Funding
During the year, the Company undertook several initiatives
to meet and manage its long term funding. Primarily in Q1,
the Company raised USD 1,000 Mn through the issuance
of 4.375%, Guaranteed Senior Notes due 2025 at an issue
price of 99.304%.
As on March 31, 2016, the Company was rated ‘Investment
Grade’ with a ‘Stable’ outlook by all three international
credit rating agencies namely Fitch, Moody’s and S&P. It
had cash and cash equivalents of ` 37,087 Mn and short-term investments of ` 30,059 Mn. During the year ended
March 31, 2016, the Company generated operating free
cash flow of ` 135,981 Mn. The Company’s consolidated net
debt as on March 31, 2016 increased by USD 1,982 Mn to
USD 12,661 Mn as compared to USD 10,679 Mn last year,
mainly on account of deferred payment liabilities to the DoT
being included in debt. The Net Debt excluding the DoT
obligations stood at USD 7,508 Mn as on March 31, 2016
i.e. it decreased by USD 884 Mn over the previous year (USD
8,392 Mn as at March 31, 2015). The Net Debt - EBITDA
ratio (USD terms LTM) as on March 31, 2016 deteriorated to
2.47 times as compared to 2.08 times in the previous year,
mainly on account of increase in debt during the year. The
Net Debt-Equity ratio increased to 1.28 times as on March
31, 2016, compared to 1.08 times in the previous year.
Awards and Recognition
- Airtel is No. 1 Telecom Company in the ‘Best Telecom
companies to Work for in India’ survey conducted by
Business Today and No. 8 across all sectors.
- Airtel has won the ‘Golden Peacock Award for
Sustainability’ for 2015. It is indeed an honour to receive
this award as it recognises Airtel’s efforts in embedding
sustainability in the services we provide; and the way we
conduct our business. This award brings Airtel a step
closer to achieving our vision of becoming the most
loved brand.
- Airtel wins Innovation Award 2016 for excellence in
Internal Auditing by the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA).
- Airtel has been honoured as the Firm of the year -
Telecommunication at the CNBC TV18 India Risk
Management Awards.
- Airtel Global Revenue Assurance & Fraud Management
team wins the Operator Excellence award in the category
of Business Innovation in Risk Management at Subex
user conference organised at Prague, Czech Republic.
Airtel wins Annual Cybermedia ICT Business Awards for
being ‘India’s Top Mobile Services Operator‘, Top Internet
Services Operator” & “Top Broadband Wireless Access
Operator” award for the year 2015.
Segment-wise Performance
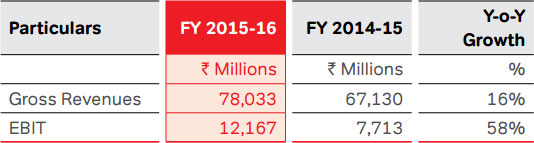
B2C services
Mobile Services: India
Overview
The last year saw significant business and regulatory
developments, which also include the release of spectrum
sharing and trading guidelines by the Department of
Telecommunications. The Company launched 3G services in
its gap circles and was the first operator to launch high speed
4G services across India. With the spectrum acquisitions
from Videocon and the proposed spectrum acquisition
from Aircel, the Company is set to become a pan-India 4G
operator. It also widened its content portfolio by launching
Wynk Movies and Wynk Games mobile application.
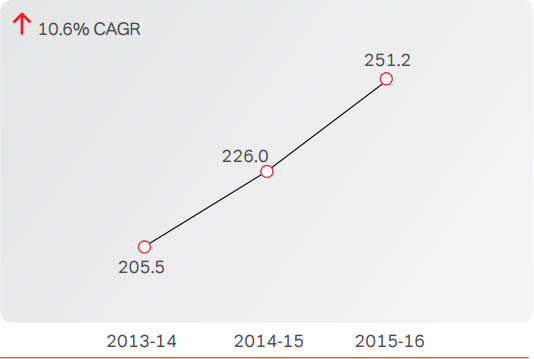
As on March 31, 2016, the Company had 251.2 Mn mobile
customers. The churn has increased to 3.4% for the current
year, compared to 2.7% during the previous year, primarily on
account of enhanced market intervention and competitive
pressure; however, it still remains the lowest in the
industry. Data revenues, as a percentage of total revenues,
significantly increased from 15.2% to 21.8% in the current
year. Of its total number of mobile subscribers, the Company
had 58.2 Mn data customers at the end of March 31, 2016,
of which 35.4 Mn were mobile broadband customers.
The segment witnessed significant improvement in the
EBITDA margin to 39.0% during the year, compared to
37.6% in the last year. Improvement in margin is primarily
due to the sustained top line growth and tighter control
over operating expenses. EBIT margin for the year declined
to 22.8%, compared to 24.0% in the last year, primarily on
account of incremental amortisation cost on new spectrum
acquired, which has an impact on EBIT margin of 2.3%.
Wireless Subscribers: India (Million)
During the year, the Company accelerated its spends on
capex, which were largely directed towards building data
capacities, increasing 3G / 4G coverage and improving the
all-round customer experience. During the year, the Company
rolled out over 63 K mobile broadband (MBB) base stations
in India. This is one of the largest global rollouts of MBB base
stations in a single year. The Company had 154,097 network
towers, compared to 146,539 network towers in the last year.
Mobile broadband (MBB) base stations were 118,197 at the
end of the year, compared to 54,381 at the end of last year.
Key Initiatives
- Airtel has introduced its new range of ‘Infinity Plans’ and
an industry first technology platform – Flexpage. While
the Infinity Plans represent an industry first plan to offer
unlimited voice calls on mobile, along with bundled
movies and music, the Flexpage is an automated
platform that allows customers to track their data usage
and get real-time usage alerts.
- Airtel launched ‘Wynk Movies’ – it’s an all new carrier
agnostic mobile application offering customers
thousands of movies and other video content. Launched
following the success of Wynk Music, the app is
India’s first curated video marketplace that offers an
exhaustive library of popular movies, TV shows and
other entertainment videos across genres. It also has a
comprehensive library of 5,000+ movies and 25,000+
videos.
- Airtel mobile moves all its prepaid mobile customers to
per second billing. Rolled out under the new Pay for What
You Use initiative as part of the Company’s Customer
First commitment, this will help ensure that customers
pay only for the time they use the Airtel network.
- Airtel revolutionised the smartphone experience for
every customer by offering irresistible data benefits
and surprises ranging from 50% daily Data ‘Cashback‘
offer, sharing of 3G / 4G packs in Family as well as
Smartphone Surprise offers; a pioneering initiative in
India. With this, Airtel has further established itself as an
undisputed preferred partner for data experience on any
smartphone.
- Airtel launched India’s first unrestricted-validity data
plan for its prepaid mobile customers. The Company
reinforced its commitment of Customers First by
enabling its prepaid users to enjoy unrestricted validity
towards consuming their data quota.
- Airtel expanded its content portfolio by launching
beta phase of ‘Wynk Games’ mobile application – the
Company’s latest OTT addition to the Wynk portfolio.
The app offers a library of over 2,000 global and local
games from across genres. ‘Wynk Games’ subscription
is free for Airtel users and at a promotional price of ` 29
for other customers in the current beta phase of the app.
- Airtel invited customers in its network modernisation
drive by, launching a microsite www.airtel.in/leap. It allows
the customers to know everything they want to know
about project leap; and get a transparent view of the
coverage of voice and high speed broadband services,
along with other details in their respective localities. This
is an industry first initiative.
- Airtel network transformation programme Project Leap
is now focusing on a series of fresh initiatives towards
creating a greener environment and building a sustainable
network for the future. The Company announced the
migration of 40,000 of its network sites across India to
green technology, while committing to bring down its
carbon emission footprint by 70% by 2018.
- Airtel became the first mobile operator in India to
commercially deploy LTE-Advanced (4G+) technology
on a live 4G network in Kerala. LTE-Advanced carrier
aggregation technology combines TD LTE (2300 MHz)
with FD LTE (1800 MHz) bandwidths to deliver mobile
data speeds up to 135 Mbps. This is also an industry first
initiative.
- Airtel announced the launch of its Platinum 3G network
for customers in the North East. Airtel’s Platinum 3G will
deliver faster internet speeds, enhance voice clarity and
offer a superior network experience for customers in the
circle.
Key Highlights
- RBI approved Payments Bank License to Airtel Payments
Bank Limited (APBL) (formerly known as Airtel Commerce
Services Limited (AMSL)). The Reserve Bank of India had
decided to grant an ‘in-principle’ approval to APBL to set
up a Payments Bank in India. APBL already offers Airtel’s
flagship semi-closed wallet under the brand name ‘Airtel
Money’.
- Airtel has acquired rights to use 2x5 MHz spectrum
in the 1800 MHz Band allotted to Videocon
Telecommunications Limited (VTL) by the Department of
Telecommunication (DoT) on April 05, 2013 for six circles,
namely, Bihar, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, UP (East), UP
(West) and Gujarat at an aggregate consideration of
` 44,280 Mn.
- Bharti Airtel Limited and its subsidiary, Bharti Hexacom
Limited entered into a definitive agreement with Aircel
Limited and its subsidiaries Dishnet Wireless Limited and
Aircel Cellular Limited to acquire rights to use 20 MHz
2300 Band 4G TD spectrum for eight circles namely,
Tamil Nadu (including Chennai), Bihar, Jammu & Kashmir,
West Bengal, Assam, North East, Andhra Pradesh and
Odisha at an aggregate consideration of ` 35,000 Mn.
The closing of the said transaction is subject to certain
customary regulatory approvals and other closing
conditions.
- Airtel signed an agreement to acquire 100% equity stake
in Augere Wireless Broadband India, which holds 20
MHz of BWA spectrum in the telecom circle of Madhya
Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
- Kotak Mahindra Bank Limited (KMBL) and Airtel
Payments Bank Limited signed the Share Subscription
and Shareholders Agreement, wherein, KMBL agreed to
acquire 19.90% of the paid-up capital of APBL.
Telemedia Services
Overview
The Company provides fixed-line telephone and broadband
(DSL) services for homes, as well as offices in 87 cities across
India. The Telemedia business witnessed a record high DSL
net addition of 309 k, seven times compared to previous year,
primarily driven by launch of innovative pricing plans and an
aggressive Go-to-Market strategy. As on March 31, 2016,
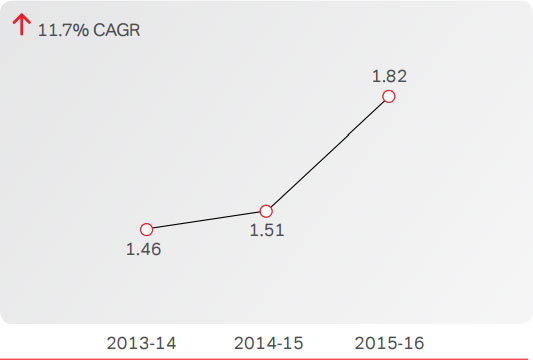
Airtel had 3.7 Mn customers. Of these, 1.8 Mn customers
subscribed to its broadband / internet services, representing
49.6% compared to 44.2% last year. The higher number of
broadband customers also resulted in a significant increase
in ARPU to ` 1,063 during the year, compared to ` 1,026
in the previous year. Consequently, non-voice revenue as
a percentage of total Telemedia revenues now represents
68.2% as compared to 64.9% in the last year.
In the Homes segment, the offerings include high-speed
broadband on copper and fibre, up to the speeds of 100
Mbps. Besides, the product portfolio also includes local,
national and international long-distance voice connectivity,
IPTV and other VAS services. Majority of the DSL Net additions
as referred above has come in the Homes Segment.
In the Corporate Business segment, Airtel is a trusted ICT
solution provider for fixed-line voice (PRIs, SIP trunking), data
solutions (ILP, MPLS, NLD) and other connectivity solutions
like Enterprise Mobility (Resource Tracking, IOT / M2M).
Additionally, the Company offers solutions to businesses
to improve employee productivity through collaborative
solutions (Audio, Video and Web Conferencing). Cloud
portfolio is also an integral part of its business solutions
suite, which offers storage, compute & Microsoft Office 365
on a pay-as-you-go model.
Broadband Users (Million)
Key Initiatives
- On the Homes front, significant progress was made
in the endeavour to pioneer high-speed broadband
through FTTH and VDSL rollouts in the top markets.
Another key intervention was improvement in the quality
of acquisition through focused interventions and plan
/ price rationalisation, resulting in lower churn. Focus
on high-speed internet during both - acquisition and
base migration, resulted in high-speed base (defined as
greater than or equal to 4 Mbps) moving to 59% at the
end of the year as against 46% last year.
- On the Corporate Business front, significant progress
was made in ICT solutions both in terms of increasing
geographic coverage - making all sites RF ready & faster
implementation with defined timelines. On product front,
layered internet offerings created for servicing customer
needs of all segments.
- Airtel rolled out irresistible offers on its home broadband
plans for existing as well as new customers, called as
“Airtel Surprises”. It enables the existing customers to
upgrade to higher speeds or additional data benefits on
their existing plans completely free of cost and enables
its new customers to avail the best possible internet
speed at their home at no extra cost.
Digital TV Services
Overview
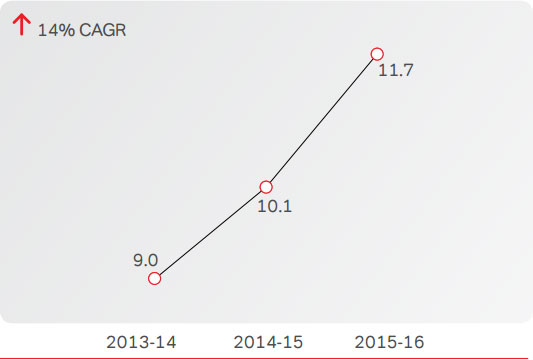
The Company served a customer base of 11.7 Mn on its
Direct-to-Home platform (Airtel digital TV), as on March 31,
2016, adding 1.7 Mn customers during the year. During
the year, the Company launched its first indigenously
manufactured set-top-boxes.
The Company currently offers both standard and high
definition (HD) digital TV services with 3D capabilities and
Dolby surround sound. The Company currently offer a total
of 504 channels including 42 HD channels, 4 international
channels and 5 interactive services. Affordability of HD set-top
boxes, demand for HD channels and upselling efforts led to
ARPU increasing by ` 19 to ` 226 as compared to previous
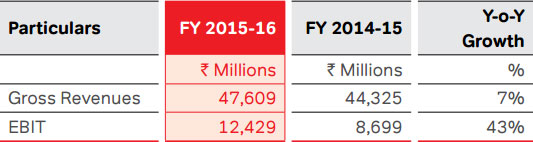
year on an underlying basis. Consequently, DTH business
turned EBIT positive on full year basis at ` 1,843 Mn compared
to EBIT losses of ` 1,581 Mn in the previous year.
Key Initiatives
- Airtel Digital TV launched its first 4K-Ultra HD (UHD)
channel. With the launch of UHD channel, Airtel enables
its customers to experience the 4 times superior picture
quality as compared to HD channels.
- Airtel Digital TV announced the launch of its first
indigenously manufactured set-top-boxes. The Made in
India set-top-boxes will be available in HD to begin with;
and soon all of Airtel Digital TV’s set-top-boxes will be
manufactured in India. With this, Airtel Digital TV has
become the latest corporate to join the Government’s
Make in India initiative, contributing to its growing
proliferation across sectors.
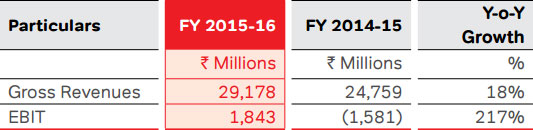
DTH Subscriber Base (Million)
B2B Services
Airtel Business
Overview
Airtel Business is India’s leading and most trusted ICT
services provider. Its diverse portfolio of services includes
voice, data, video, network integration, data centre, managed
services, enterprise mobility applications and digital media.
Airtel Business consistently delivers cutting-edge integrated
solutions, superior customer service and unmatched depth
/ reach to global markets, to enterprises, governments,
carriers, and small and medium businesses.
Revenues in this segment include those from: a) Enterprise
& Government Business (EGB), which is predominantly
Data, and b) Global Business which includes wholesale voice
and data. The EGB revenues (included in Airtel Business)
together with the Corporate Mobile revenues (included in
India Mobile) and Corporate Fixed Line revenues (included
in Telemedia) is ` 92,327 Mn in this year; this is now 13.0%
of the total India revenues, and has grown by 18.8% over
the last year.
Global Business, the international arm of Airtel Business,
offers an integrated suite of global and local connectivity
solutions, spanning voice and data to the carriers, Telcos,
OTTs, large multinationals and content owners globally.
Airtel’s international infrastructure includes the ownership of
i2i submarine cable system, connecting Chennai to Singapore
and consortium ownership of SMEWE4 submarine cable
system, which connects Chennai and Mumbai to Singapore
and Europe. It also includes cable system investments like
Asia America Gateway (AAG), India, the Middle East and
Western Europe (IMEWE), Unity, Europe India Gateway (EIG)
and East Africa Submarine System (EASSy). Along with
these seven owned subsea cables, Airtel Business has a
capacity on 20 other cables across various geographies.
Its global network runs across 225,000 Rkms with over
1,000 customers, covering 50 countries and five continents.
This is further interconnected to its domestic network and
direct terrestrial cables to SAARC countries and China,
helping accelerate India’s emergence as a preferred transit
hub. Global business now serves more than 60% of the
SAARC internet requirement.
Leveraging the direct presence of Airtel in 20 countries
across Asia and Africa, Global Business also offers mobile
solutions (ITFS, signalling hubs, messaging), along with
managed services and SatCom solutions.
Key Initiatives
- Airtel has launched Smart MPLS services, wherein
customers would be provided access to application
performance management in addition to network
performance management.
- Global Business has launched Direct Internet Access
(DIA) product in partnership with various global
carriers. The DIA product would enable global telecom
organisations to deal multiple providers, multiple billings
and different SLA when procuring local Internet for their
customers across multiple countries.
- Airtel launched a unique, one-of-a-kind gamut of corporate
applications known as EAS- Enterprise Application store,
which will empower an enterprise by providing the one
stop shop experience to achieve its mobility objectives,
provide completely online / touch free consumption and
self-care for enterprise application user.
- Airtel launched the digital engagement solutions with
long-term contracts in the government space. Main
pillars of the solutions, include IVR, USSD, Bulk SMS and
toll-free internet.
- Airtel continued its drive to localise the content, which
improves user experience, along with lowering the cost
of accessing content. Airtel now serves more than 50%
internet requirements from India and have partnered
with various global OTTs for content delivery service.
- Airtel has expanded its cloud service portfolio with the
launch of Connexion, which will ensure a more secure,
scalable and seamless private connection between
enterprises, cloud service providers, and data centre
partners. This will help customers seamlessly and
more securely connect to Microsoft Azure, by bringing
down their network cost substantially and improving
performance.
- Airtel has strategic tie-ups with various global operators for
satellite business. The objective is to reach destinations,
where we have limited or unreliable connectivity. Airtel is
focusing primarily on satellite communication, media and
broadcast solutions, along with managed solutions and
consulting projects.
- Airtel is adding new capacity in new and existing cables
assets in the Pacific and Atlantic routes to further expand
its footprint globally.
- Airtel has launched two new POP in Kenya and South
Africa for IP Transit and MPLS services.
Key Highlights
- Innovations like ‘Call me free’ and ‘Share credit with
friends’ in Airtel Talk helped in winning ‘Innovations
Award’ in the Consumer Services category at the Global
Telecom Awards 2016, London.
- Airtel Talk also won the Gold Stevie Award in the ‘Utility and
Services app’ category at the 12th annual International
Business Awards, 2015. Stevie’s is one of the world’s
most prestigious awards and celebrates distinguished
accomplishments of companies worldwide.
- Airtel Corporate Business won Frost & Sullivan ICT Award
for the second year in a row.
- Airtel Business has won the coveted Aegis Graham
Bell Award for its mHealth solution. mHealth solution
aims to improve the delivery of primary health services,
specifically for expecting mothers in rural India, by
leveraging technology. The application successfully
works in tandem with the National Rural Health Mission’s
(NRHM) initiatives to improve local health indices and
quality of life.
Passive Infrastructure Services
Overview
Bharti Infratel Limited, a subsidiary of Bharti Airtel, provides
passive infrastructure services on a non-discriminatory basis
to all telecom operators in India. Bharti Infratel deploys, owns
and manages telecom towers and communication structures
in 11 circles of India. It also holds 42% share in Indus Towers
(a joint venture between Bharti Infratel, Vodafone and Idea
Cellular). Indus Towers operates in 15 circles (four common
circles with Bharti Infratel, 11 circles on an exclusive basis).
Hence, the Company has a nationwide presence with
operations in India’s all the 22 telecommunications circles.
As on March 31, 2016, Bharti Infratel owned and operated
38,458 towers, while Indus Towers operated 119,881
towers. Bharti Infratel’s towers, including its 42% interest
in Indus Towers, comprised an economic interest in the
equivalent of 88,808 towers in India, as on March 31, 2016.
Bharti Infratel is listed on the Indian Stock Exchanges, NSE
and BSE.
Africa
Overview
The revenue-weighted currency depreciation versus the US
Dollar across 17 countries in Africa over the last 12 months
(exit March 31 rates) has been 5.7%, primarily caused by
the depreciation in Malawi Kwacha, Zambian Kwacha and
Tanzanian Shilling. In terms of the 12-month average rates,
the revenue-weighted Y-o-Y currency depreciation has been
18.3%, primarily caused by the depreciation in Zambian
Kwacha, Nigerian Naira, CFA, Malawi Kwacha and Ugandan
Shilling. To enable comparison on an underlying basis, all
financials up to PBT and all operating metrics mentioned
below are in constant currency rates as on March 05, 2015
for all the periods. (PBT as mentioned below excludes any
realised / unrealised derivatives and exchange gain or loss
for the period).
During the year, sale and lease back of 8,740 towers in
seven countries was completed for a total consideration of
USD 1.8 Bn.
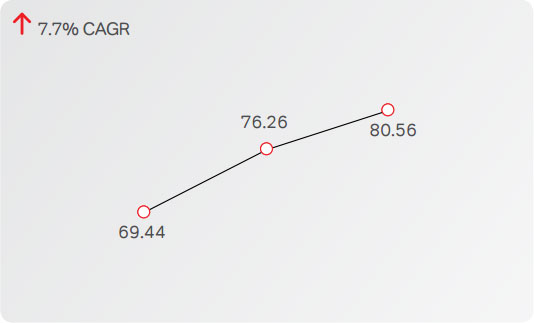
As on March 31, 2016, the Company had 80.6 Mn customers
in Africa across 17 countries, compared to 76.3 Mn customers
in the previous year, an increase of 5.6%. The total minutes
on the network during the year increased by 14.7% to 136.0
Bn, compared to 118.6 Bn in the previous year. At the end of
the year, 15.8 Mn data customers accounted for 19.6% of
the total customer base, compared to 16.1% in the previous
year (on the basis of revised definition of ‘data customer’ as
one who uses at least 1 MB in last 30 days). Data traffic had
been more than doubled to 74.0 Bn MBs from 35.3 Bn MBs
in the previous year with usage per customer increasing from
277 MBs to 435 MBs. Voice realisation per minute, however,
declined from 2.53 cents to 2.14 cents for the full year, due
to competitive pressures. Consequently, the overall ARPU in
Africa declined from USD 4.6 to USD 4.2. Total sites in Africa
as on March 31, 2016 were 20,196 (PY: 18,819), of which
13,128 (PY: 10,011) were 3G sites, representing 65% of the
total sites, compared to 53% for the previous year.
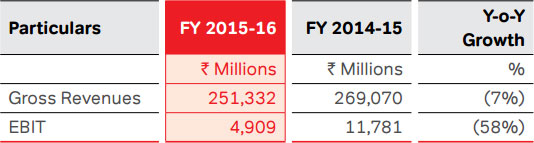
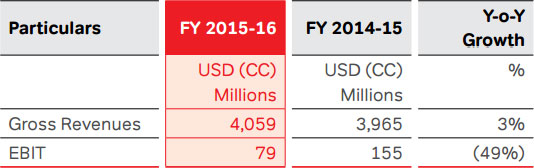
The revenues of Airtel Africa grew by 3.1% to USD 4,059
Mn, compared to USD 3,935 Mn in the last year (growth
of 4.2% adjusting for the impact of divestment of tower
assets). Underlying EBITDA at USD 906 Mn (PY: USD 869
Mn) reflected a similar margin of 22.1%, compared to the
previous year. EBIT at USD 79 Mn was lower in comparison
to USD 155 Mn in the previous year, primarily due to lower
EBITDA. After accounting for the full year capex of USD
771 Mn (PY: USD 1,066 Mn), operating free cash flow was
USD 81 Mn, compared to cash burn of USD 197 Mn in the
previous year.
Wireless Subscriber: Africa (Million)
Key Initiatives
- Airtel Kenya launched a new plan, which offers flat rate
for roaming across Africa. One Airtel provides flexible
and simple tariff within the Airtel Network footprint. The
customers of Airtel Kenya roaming in 16 Airtel Africa’s
countries will be treated as local customers on the visited
network in terms of pricing, including receiving calls free
of charge, while retaining their home SIM card.
- Airtel Ghana launched the first ever tap-and-pay mobile
money payment service in Ghana. The OpCo has
added another first to its credits, as it has rolled out an
innovative service through its Airtel Money that allows
a tap-and-pay, contactless payment, based on the Near
Field Communications (NFC) technology.
- Airtel signed a three-year global agreement with the
World Food Programme for cash and value voucher
distribution services in Madagascar, Malawi, Tanzania,
DRC, Congo B and Zambia.
- Airtel DRC and Korongo Airlines have signed an
agreement for air tickets purchase through Airtel
M-Falanga - Airtel Money.
- Airtel Africa partners with customer engagement
software provider IMImobile, to launch Airtel Artist
Management System. The Airtel Artist Management
System is a new service innovation, enabling upcoming
music artists to upload and make available their music to
potential audiences out of its 83 Mn subscribers.
- Airtel DRC & UBA officially launch ‘LIBIKI’, the new
microloan service through mobile phones. LIBIKI is the
new Airtel Money services, which offer small amount of
loans to the entrepreneurs or craftsmen, who have no
access to the bank credit system.
- Airtel and I&M Bank Ltd have announced a partnership
that enables I&M Bank customer’s access to their
accounts via Airtel Money free of charge. The Bank
account holders will now be able to pull money from their
bank accounts into their Airtel Money wallets or push
money from their Airtel Money wallets to their I&M Bank
accounts.
- The year has continued to see Airtel’s involvement in the
community across Africa, such as:
- Airtel Kenya participated in the First Lady’s half
marathon aimed at eradicating maternal deaths by
providing better healthcare systems for pregnant
mothers.
- Airtel Chad together with UNICEF launched and
executed a nationwide campaign to fight Malaria,
Ebola and Cancer.
- Airtel led a breast cancer awareness campaign in
partnership with the Think Pink Foundation.
- Airtel Zambia donated various items for the
Malnutrition ward as well as food stuff for the cancer
ward.
- Airtel Kenya reached 43 schools with free internet
connectivity.
- Airtel Ghana helped millions of flood victims by giving
them an opportunity to communicate with their loved
ones and friends for free through an emergency offer,
‘Airtel Too Much Relief‘ Pack.
Key Highlights
- Airtel and Liquid Telecom signed pan-African agreement
to provide fibre connectivity to towers. Airtel’s mobile
broadband subscribers in Africa will soon enjoy faster
Internet access speeds on its 3G and 4G networks.
The framework agreement enables Airtel operations
to leverage Liquid Telecom’s existing 20,000 km-long
fibre network across East, Central and Southern Africa,
as well as enjoy new purpose-built fibre infrastructure,
to connect Airtel’s mobile base stations and enterprise
customers with fibre.
- During the year, sale and lease back of 8,740 towers in
seven countries (Ghana, Uganda, Kenya, Burkina Faso,
Zambia, Nigeria and Congo B) was completed for a total
consideration of USD 1.8 Bn (sale and lease back to Eaton
tower – 2,681 towers for USD 0.54 Bn, IHS towers - 949
towers for USD 0.15 Bn, Helios towers - 393 towers for
USD 0.05 Bn and ATC – 4,717 towers for USD 1.06 Bn).
- Airtel has signed a definitive agreement with Orange to
sell its operations in Burkina Faso and Sierra Leone. The
companies had signed an initial agreement in July 2015
for the acquisition of Airtel’s operations in Burkina Faso,
Sierra Leone, Chad and Congo B. The agreement over
the latter two countries has lapsed.
- The Company’s subsidiary in Tanzania and American
Towers Corporation and its subsidiaries have entered
into an agreement for the sale of over 1,300 telecom
towers in Tanzania.
- Airtel Rwanda in a drive to extend affordable
telecommunications products and services to Rwandans,
has partnered with ITEL to introduce a new trendy and
affordable data enabled phone dubbed KEZA. It now
stands as one of the most affordable data enabled
phones in the Rwandan market.
Awards & Recognition
- Airtel Rwanda received the award of best 4G Mobile
Network Operator for 2015 for exceptional performance
in 4G LTE.
- Airtel Money Malawi was commended for being the
mobile financial services leader in Malawi at 62.2%
market share by Malawi Communications Regulatory
Authority in conjunction with the National Statistical
Office.
- Airtel Money Seychelles won the best innovative product
in the Seychelles chambers of commerce award (SCCI)
in November 2015.
- Airtel Tanzania has lifted awards in a recent Tanzania
Leadership Awards 2015. Airtel emerged winners in two
categories, the best use of social media in marketing
and brand excellence within the telecom sector in the
country.
- Airtel Sierra Leone has received an award in recognition
of the role the Company played in the fight to contain
and eradicate the Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) from the
Office of the President.
- Airtel Ghana was bestowed with four awards at the 2015
Ghana Telecom Awards. The Company has won these
awards for five consecutive years. Airtel Ghana swept
awards in the following categories - Telecom Brand of
the Year; Marketing Campaign of the Year - Talk Chaw;
Innovative Enterprise Product of the Year - One Network
and Special Recognition to the Telecom Industry Award -
Lucy Quist.
- Airtel Nigeria emerges Telecom Company of the Year for
its laudable contributions to the growth of the telecoms
industry in Nigeria. Airtel Nigeria has been named
Africa’s Telecommunications Company of the Year at the
6th African Business Leadership Forum & Awards 2015.
- Airtel Uganda won two awards at the Digital Impact
Awards Africa for its innovations in the Finance and
Entertainment sector. Airtel Uganda’s mobile money
transaction service was recognised and awarded in the
category of Best Financial Inclusion Impact. The talent
search music competition, Airtel Trace Music Star, was
recognised in the category of the Best Digital Marketing
Campaign.
- Airtel Money Tanzania was recognised for the Best
Mobile Money Product Innovation at Kalahari mobile
money awards.
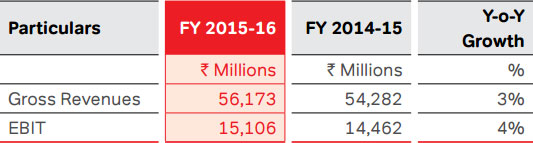
South Asia
Overview
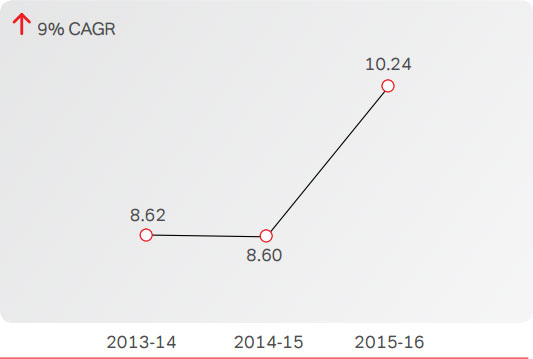
As on March 31, 2016, South Asia had 10.2 Mn mobile
customers on the Company’s network. Data customers
represented 28.7% of the total customer base as on March
2016, compared to 25.5% in the last year (on the basis of
revised definition of ‘data customer’ as one who uses at least
1 MB in last 30 days). As on March 2016, the Company had
7,083 sites on network, compared to 6,867 sites in the last
year. Of the total number, 3G sites were 4,115 (PY: 3,050) in
number, representing 58.1% of the total sites, compared to
44.4% for the previous year.
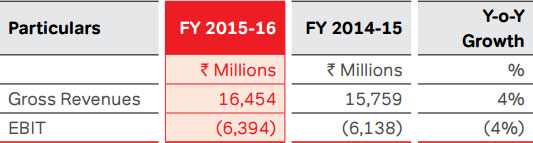
The Company’s full year revenues of South Asia increased
by 4.4% to ` 16,454 Mn, compared to ` 15,759 Mn in the
previous year. EBITDA loss for the year was at ` 801 Mn,
compared to a loss of ` 196 Mn in the previous year. EBIT
losses for the year reported at ` 6,394 Mn, compared to a
loss of ` 6,138 Mn in the previous year. Capex for the year
was ` 3,321 Mn, compared to ` 3,233 Mn in the previous
year
Key Initiatives
- Airtel Sri Lanka commenced 2016 by being the
Principal Sponsor of the Battle of the North (annual
cricketing tournament) for the third consecutive year.
- Airtel Sri Lanka launched Smart Byte facility in order
to facilitate customers to enjoy data usage at
discounted rates.
- Airtel Sri Lanka won a Gold Award for the Best
Multinational Corporations in Sri Lanka and silver award
for Medium Sized Enterprise Category. Airtel Lanka
is the youngest organisation in terms of market
existence in Sri Lanka to receive these prestigious
accolades; and the only telecommunication operator to
be listed on the GPTW (Sri Lanka) Hall of Fame.
Wireless Subscriber: South Asia (Million)
- Axiata Group Berhad and Bharti Airtel Limited signed
a Definitive Agreement to merge their respective
telecommunication subsidiaries in Bangladesh, namely,
Robi Axiata Limited (Robi) and Airtel Bangladesh
Limited (Airtel). The agreement followed the September
09, 2015 announcement of both parties entering into
an exclusive discussion to explore the possibility of
combining the business operations in Bangladesh.
- Airtel Bangladesh has won the prestigious Asia
Communication Award 2015 in the Category of
‘Customer Experience Initiative’ for ‘Online Airtel
Experience Centre’.
Risks and Concerns
At Bharti Airtel (the Company), we have thrived globally
by building a culture of innovation and high performance.
We explore new markets and business models across
the world; evolve new ways of customer and stakeholder
engagement; enter into new strategic partnerships; adopt
new technologies; and build exponential efficiencies in
existing systems. While these initiatives unveil a universe
of possibilities, potential risks and uncertainties arise in a
volatile business environment. The distress signals need to
be addressed with urgency for smooth operations. Therefore,
we have created a robust risk management framework
in our operating landscape. We have a sound practice to
identify key risks across the Group and prioritise relevant
action plans for mitigation.
At the Board Governance level, the Risk Management
Framework is reviewed bi-annually by the Company’s Risk
Management Committee. The Board of Directors performs
an annual review. These apex reviews include: discussing the
management submissions on risks, prioritising key risks and
approving action plans to mitigate such risks. The Internal
Audit function is responsible to assist the Risk Management
Committee on an independent basis with a full status of
risk assessments and management. Every quarter, the Risk
Management Committee also obtains periodic updates on
certain identified risks, depending upon the nature, quantum
and likely impact on the business.
At the Management level, the respective CEOs for the
Management Boards (AMB and Africa Exco) are accountable
for managing risks across their respective businesses,
viz., India and South Asia, and Africa. The strategic risk
registers capture the risks identified by the operating teams
(Circles or Operating Companies) as well as the functional
leadership teams at the national level. The AMB / Africa Exco
ensure that the environment – both external and internal – is
scanned for all possible risks. Internal Audit reports are also
considered for identification of key risks.
The two CEOs, for India & South Asia and Africa, are responsible for the implementation of the agreed risk
framework, including the detailed processes of:
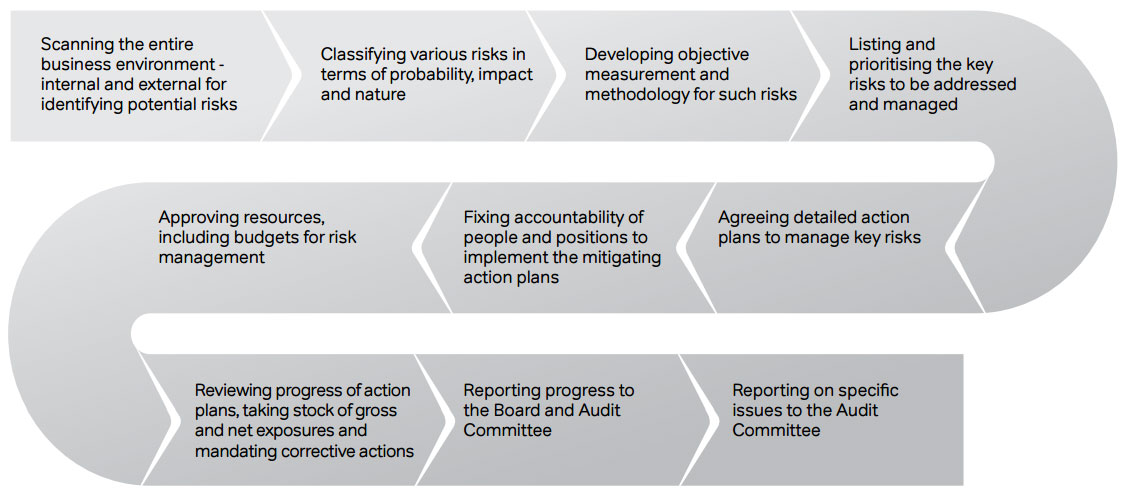
At the operating level, the Executive Committees (EC) of
Circles in India and Operating Companies in the international
operations are entrusted with responsibilities of managing
the risks at the ground level. Every EC has local representation
from all functions, including many centrally driven functions
like IT, Legal & Regulatory, Finance and SCM, besides
customer-facing functions, such as Customer Service, Sales
& Distribution and Networks. It is the responsibility of the
Circle CEO or Country MD to pull together various functions
and partners to manage the risks. They are also responsible
for identification of risks, and escalating it to the Centre for
agreeing mitigation plans. Operating level risk assessments
(RACM) have been concluded at Function / OpCo risk
assessment and mitigation plans agreed and kicked off.
Internal Audit Plans are being drawn up to ensure scope and
coverage of these critical risks during the course of next year.
The key risks that may impact the Company and the
mitigating actions undertaken by the Company comprise:
1. Regulatory and Political Uncertainties (Legal &
Compliance)
Risk Statement
The Company operates in India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and
17 African countries. Some of these countries (or regions
within countries) are affected by political instability, civil
unrest and other social tensions. The political systems in a few
countries are also fragile, resulting in regime uncertainties;
hence, the risk of arbitrary action. Such conditions tend to
affect the overall business scenario. In addition regulatory
uncertainties, like escalating spectrum prices, call drops /
EMF penalties, among others are potential risks facing the
business.
Mitigation
- As a responsible corporate citizen, we engage
proactively with key stakeholders in the countries in
which we operate; and continuously assess the impact
of the changing political scenario. We contribute to the
socio-economic growth of the countries in which we
operate through high-quality services to our customers,
improved connectivity, providing direct and indirect
employment, and contributions to the exchequer. Our
annual Sustainability Report is a document, which
highlights to the larger external environment the role
we are playing in the countries we are operating in.
We maintain cordial relationships with governments
and other stakeholders in every country where we
operate. The Country MDs and Circle CEOs carry direct
accountability for maintaining neutral Government
relations. Through our CSR initiatives (Bharti Foundation
etc.), we contribute to the social and economic
development, especially in the field of education.
- We actively work with industry bodies like COAI, CII, and
FICCI on espousing industry issues e.g. penalties, right
of way, tower sealing, and so on.
2. Economic Uncertainties (Operational)
Risk Statement
The Company’s strategy is to focus on growth opportunities
in the emerging and developing markets. These markets
are characterised by low to medium mobile penetration, low
internet penetration and relatively lower per capita incomes,
thus offering more growth potential. However, these
countries are also more prone to economic uncertainties,
such as capital controls, inflation, interest rates and currency
fluctuations. Since the Company has borrowed in foreign
currencies, and many loans are carrying floating interest
terms, we are exposed to market risks, which impact our
earnings, cash flow and balance sheet. These countries
are also affected by economic downturns, primarily due to
commodity price fluctuations, reduced aid, capital inflows
and remittances. Slowing down of economic growth tends
to affect consumer spending, including telecom.
Mitigation
- As a global player with presence across 20 countries,
we have diversified our risks and opportunities across
markets.
- Through a variety of services including voice, data,
Airtel Money and value added services, we have also
spread our portfolio.
- To mitigate currency risks, we follow a prudent risk
management policy, including hedging mechanisms
to protect our cash flow. No speculative positions
are created; all foreign currency hedges are taken on
the back of operational exposures. A prudent cash
management policy ensures that surplus cash is upstreamed
regularly to minimise the risks of blockages
at times of capital controls. We have specifically
renegotiated many operating expenditure / capex
Fx contracts in Africa and converted them to local
currency, thereby reducing Fx exposure.
- To mitigate interest rate risks, the Company is further
spreading its debt profile across local and overseas
sources of funds and to create natural hedges.
- Finally, the Company adopts a pricing strategy that is
based on twin principles of mark to market, profitability
and affordability, which ensures that we protect margins
at times of inflation, and market shares at times of
market contraction.
3. Poor Quality of Networks and Information
Technology Including Redundancies and Disaster
Recoveries (Operational)
Risk Statement
The Company’s operations and assets are spread across
wide geographies. Our telecom networks are subject to risks
of technical failures, partner failures, human errors, or wilful
acts or natural disasters. Equipment delays and failures,
spare shortages, energy or fuel shortages, software errors,
fibre cuts, lack of redundancy paths, weak disaster recovery
fall-back, and partner staff absenteeism, among others are
few examples of how network failures happen. Repeated
outages and / or poor quality of networks cause disruption
of services, resulting in revenue losses, customer attrition,
market share losses and damage to brand image and
Company reputation. Regulators are now also levying stiff
monetary penalties for poor quality of services.
The Company’s IT systems are critical to run the customerfacing
and market-facing operations, besides running
internal systems. In many geographies or states, the quality
of IT connectivity is sometimes erratic or unreliable, which
affect the delivery of services e.g. recharges, customer
query, distributor servicing, customer activation, billing, etc.
In several developing countries, the quality of IT staff is
rudimentary, leading to instances of failures of IT systems
and / or delays in recoveries. The systems landscape is ever
changing due to newer versions, upgrades and ‘patches’ for
innovations, price changes, among others; the dependence
on IT staff for turnaround of such projects and changes is
huge. Unauthorised access to network and IT systems can
result in wrong configurations, poor quality of service, frauds
and regulatory non-compliances.
Mitigation
- Network Planning is increasingly being done in-house,
to ensure that intellectual control on architecture is
retained within the Company. The recently announced
` 600,000 Mn Leap Programme in India continuously
seeks to address issues (congestion, indoor coverage,
call drops, modernisation and upgrade of data speeds,
among others) to ensure better quality of network.
Recent efforts also include transformation of the
microwave transmission, fibre networks, secondary
rings / links and submarine cable networks. The
Company consistently eliminates systemic congestion
in the network, and removes causes of technical
failures through a quality improvement programme,
as well as embedding redundancies. Tighter SLAs are
reinforced upon network partners for their delivery. The
Company’s Network Team performance is measured,
based on network stability, customer experience and
competitor benchmarking. The Revenue Assurance
team constantly monitors revenue leakages due to
failure of systems or configuration errors. The Company
follows a conservative insurance cover policy that
provides a value cover, equal to the replacement values
of assets against risks, such as fire, floods, and other
natural disasters.
- In Africa, a sustained concentrated investment
programme started in FY 2015-16 based on market
revenue mapping will ensure that our network quality
in these areas are comparable if not better than
competition.
- The Company’s philosophy is to share infrastructure
with other operators, and enter into SLA-based
outsourcing arrangements. We have been proactively
seeking sharing relationships on towers, fibre, VSAT, data
centres and other infrastructure. The disposal of towers
in Africa to independent and well-established tower
companies and long-term lease arrangements with
them will ensure high quality of assets and maintenance
on the passive infrastructure. We have also put in place
redundancy plans for power outages, fibre cuts, VSAT
breakdowns, and so on, through appropriate backups
such as generators, secondary links, among others.
Similar approaches are deployed for IT hardware and
software capacities; and internal IT architecture teams
continuously reassess the effectiveness of IT systems.
- Information Security is managed by dedicated
IT professionals, given the huge dependence on
automated systems, as well as to ensure that customer
privacy is protected.
4. Inadequate Quality of Customer Lifecycle
Management from Acquisition to Churn
(Operational)
Risk Statement
In a market dominated by prepaid customers, several
inefficient processes have crept in over the years across the
industry, in respect of customer acquisitions. Such practices
are resulting in high rotational churn, high acquisition costs,
low lifetime value of new customers, diversion of focus of
sales force on acquisitions, rather than revenue generation,
trade frauds, among others.
Customer mind-sets and habits are shifting rapidly, reflected
in their ever-rising expectations in terms of quality, variety,
features and pricing. The competitive landscape is also
changing dramatically, as operators vie with one another
to capture customer and revenue market shares. Failure
to keep pace with customer expectations would result in
customer churn, leading to erosion of revenues, profits and
cash flows; and market share losses.
Mitigation
- Improved customer acquisition process like monitoring
new customer acquisition churn, high acquisition
recharge denominations, direct distribution, trade
margins structures and so on have been introduced.
- The Company constantly refreshes its ways of
working, especially in customer service, innovation,
marketing and distribution. These are now captured
in the Company’s integrated Customer Lifecycle
Management approach, which ensures that every
customer’s behaviour is studied, classified and
segmented, followed by segmented service and price
offerings. Organisational effectiveness is enhanced
through appropriate design and creation of leaner
and multi-functional teams. Technologies and tools
(business intelligence, scientific pricing models) are
deployed in managing the customer lifecycle.
5. Non-compliance with Subscriber Verification
and KYC Regulations (Operational)
Risk Statement
Regulators are introducing more stringent subscriber
verification and KYC guidelines, including verification
processes capturing biometrics, such as retina scan,
fingerprints, among others. The quality of KYC documents
is also being stringently scrutinised. Non-compliance with
these guidelines entail severe penalties, which is reflected by
instances of such actions by regulators on other operators.
Mitigation
- The Company is investing significantly in KYC tools,
including biometric scanners to improve the quality of
subscriber activation and documentation processes
as per required legislation. Self-compliance and
reinforcing of ‘tone at the top’ to ensure compliance is
the bedrock of our control. Focus on quality of partners
and IT systems, staff training, proactive maker-checker
controls and internal audits, as well as robust internal
MIS help achieve adherence to compliances. Internal
MIS on compliance scores, activation time taken, etc.
has been standardised to achieve greater focus on
compliances. Staff involved in such processes have
been revamped to reflect clear responsibilities for
compliance to verification and KYC guidelines. Severe
management action is taken in case of any noncompliance.
6. Increase in Cost Structure (Capex / Operating
Expenditure) Ahead of Revenues (Operational)
Risk Statement
Across markets, costs structures have been increasing both
from volumes (new sites rollouts, capacity) or / and rate
increases (inflation, Fx impacts, wage hikes and so on). These
costs may not be naturally compensated through revenue
increases, which are linked to telecom mark to market issues
e.g. market tariffs, competitive positions, and idle capacities.
Consequently, Company margins / cash flows can come
under pressure, putting the financial health of a Company
at risk.
Mitigation
- The Company has institutionalised the War on
Waste (WOW) Programme, an enterprise-wide cost-reduction
programme. This has been rolled out across
all functions and countries. All functions / countries
are targeting cost reductions and cost efficiencies.
Capex Committees have been introduced, ensuring
stringent monitoring of capex proposals. The proposals
now systemically need to cover issues like revenue
generating capex ratio, capex trigger, risks, alternates,
competitors, among others.
- Reduction in capex spends and improvement in capex
productivity has happened with significant programmes
like ICR, fibre sharing IRU, fibre co-build and Africa tower
disposal.
- The Company has introduced more science into the
decision-making criteria for investments in new sites.
7. Entry of New Competition with Disruptive
Business Models (Strategic)
Risk Statement
Entry of any new operators, including MVNOs into an already
crowded telecom market is a potential risk. Entry of new
operators into the market will create surplus capacities,
leading to pricing pressures in the industry; and at the same
time accelerate customer migration from legacy 2G / 3G
networks. This may put pressure on margins / cash for the
Company, in the short term before industry consolidates and
/ or the surplus capacity is absorbed.
Mitigation
- Airtel has prided itself on being the # 1 network
operator across the country. Its long term spectrum
strategy, based on future technologies and consumer
needs have been ahead of the market. The Company
in Q3’15, was the first 4G operator to launch 4G across
India in 296 cities, firming its positions as the only 4G
operator in the country. The Company has become the
only company with 3G spectrum across 21 of the 22
circles in India. A record breaking 63,816 broadband
data sites were rolled out across India this fiscal, which
is well ahead of all the operators. Airtel has also been
the preferred network for high value customers; and
has the highest ARPU in the industry. The Company has
strategic programmes for driving down churn through
an integrated and end-to-end experience through sharp
propositions for high-value customers.
8. Issues Arising out of Emerging Businesses and
New Technologies (Strategic)
Risk Statement
Evolving technologies result in change in customer value
propositions. The quality of internet experience, especially in
a seamless manner and indoor environment has emerged as
a key competitive parameter. Digital content and apps have
now become the favourites for mobile customers. Digital
Mobile money technologies, innovative mobile apps, Cloud,
M2M, SaaS and other technology-based VAS products
are also evolving. Such rapid technology evolution may
impact the functionality of existing assets and accelerate
obsolescence. Keeping pace with changing customer
expectations is a big agenda for the telecom sector
There is also a serious risk of unavailability of right skills to
grow these emerging businesses and / or deploy the new
technologies. Talent availability in emerging economies is
also limited, since the overall demand for good talent far
outstrips the supply, specifically for IT and Networks, affecting
the performance of our partners also. In addition, there is a
need for constantly upgrading skills and competencies of the
existing work force. Skill mismatch leads to failed launches,
ill-planned projects, sub-optimal cost structures, faulty asset
configurations, among others, which in turn leads to financial
losses.
Mitigation
- Airtel’s strong strategic vendor relationships – especially
in the areas of network technologies, IT, mobile money
and a few other key VAS technologies help us keep pace
with technology shifts and retain market leadership. The
Company’s own digital innovations such as Wynk under
which OTT apps like Music, Movies and Gaming have
been launched, My Airtel App, etc. are few examples of
its keeping pace with the changing landscape.
-
The potential risks of asset obsolescence are managed
through leaner order pipelines, demand-based capacity
sourcing and formal swap arrangements with vendors.
In several countries, the Company is proactively leading
the development of 3G, 4G, digital content partnerships,
mobile money, among others ahead of the curve to
leverage big opportunities. The Company has also
entered the digital payments space with the receipt of a
Payments Bank license, which will enable it to become
a key player in this rapidly evolving ecosystem.
9. Adverse Regulatory Taxation or Fiscal Taxation
Developments including Risks Related to Tax
Positions (Legal & Compliance)
Risk Statement
Regulatory developments in India, South Asia and Africa can
pose several challenges to the telecom sector. The telecom
sector is highly taxed with high revenue share-based license
fees and significant spectrum acquisition costs in auctions,
multiple levies, such as service taxes, excise duties, Sim tax,
VAT, and so on. The corporate tax rates on profits, combined
with withholding taxes on remittances have made the
overall tax structure extremely heavy. In several countries,
tax litigations are getting prolonged due to ambiguous
interpretations and / or lack of judicial precedents. In some
countries, which are undergoing economic challenges,
unfortunately, the telecom industry is being seen as a ‘cash
cow’. The stringent regulatory requirements in respect
of rollout / coverage and quality of services accompanied
by unreasonable demands also pose another threat. Such
adverse regulatory or taxation developments have affected
the telecom sector, including the Company.
Mitigation
The Company has always stood for a fair, transparent and non
– discriminatory government policy on telecom regulation. It
has insisted governments of all countries that sustainable
regulatory regimes will lead to a healthy growth of the sector,
leading to higher investments and modernisation, which
in turn benefits the industry and society. The Company
stands for a regime that promotes healthy, competitive
pricing keeping two objectives in mind – customer interests
and health of the sector. As an industry participant the
Company provides adequate facts and figures to prove how
healthy telecom growth strengthens a country’s economic
growth. The Company has been at the forefront of industry
cooperation to share infrastructure, minimise impact on
the environment, lower operational cost and make services
more affordable. As a responsible operator, the Company
participates in government consultation and industry
association events, to foster collaboration and knowledge
sharing for best industry policies and practices.
10. Gaps in Internal Controls (Financial and Nonfinancial)
– (Operational)
Risk Statement
.
The Company serves over 357 Mn customers globally with
a daily average of 4,037 Mn minutes of voice and 1,887
terra bytes of data carried on wireless networks located at
more than 181,000 sites. Gaps in internal controls and / or
process compliances not only lead to wastages, frauds and
losses, but can also adversely impact the Airtel brand.
Mitigation
- Airtel’s business philosophy is to ensure compliance
with all accounting, legal and regulatory requirements
proactively. Compliance is monitored meticulously
at all stages of operation. Substantial investments in
IT systems and automated workflow processes help
minimise human errors.
- Besides internal audits, we also have a process of self-validation
of several checklists and compliances as
well as a ‘maker-checker’ division of duties to identify
and rectify deviations early enough. The Company has
also implemented GRC systems (Governance, Risk and
Compliance) to embed systemic controls.
The Company has introduced Internal Financial
Controls and the Corporate Audit Group has tested
such controls. The Audit Group has asserted that the
Company has in place adequate tools, procedures and
policies, ensuring orderly and efficient conduct of its
business, including adherence to Company’s policies,
safeguarding of its assets, prevention and detection
of frauds and errors, accuracy and completeness of
accounting records; and timely preparation of reliable
financial information.
Internal Controls
The Company’s philosophy towards internal controls is
based on the principle of healthy growth with a proactive
approach to risk management.
The Circle and Country Finance Heads are held accountable
for financial controls, measured by objective metrics
on accounting hygiene and audit scores. They are fully
responsible for accuracy of books of accounts, preparation
of financial statements and reporting the same as per
the Company’s accounting policies. Regulatory and
legal requirements, accounting standards, and other
pronouncements are assessed regularly as to whether and
to what extent they are relevant and their related impact on
financial reporting. The relevant requirements are defined in
the Group Accounting Manuals, which are communicated
to relevant units and, together with the financial reporting
calendar evidencing the tasks and timelines that are binding
throughout the Group, forms the basis of the financial
reporting process.
The Company deploys robust system of internal controls
that facilitates fair presentation of our financial results in
a manner that is complete, reliable and understandable,
ensure adherence to regulatory and statutory compliances,
and safeguards investor interest by ensuring the highest
level of governance and periodic communication with
investors. M/s. S.R. Batliboi & Associates LLP, our Statutory
Auditors, have done an independent evaluation of key
controls over financial reporting (ICOFR) and expressed
an unqualified opinion stating that the Company has, in
all material respects, adequate internal financial control
system over financial reporting; and such internal financial
controls over financial reporting were operating effectively
as on March 31, 2016. Independent validation was also led
by Corporate Audit Group for assessing the effectiveness of
Internal Financial Controls (IFC) and no reportable material
weaknesses in the design or operation were observed.
The Company has in place an Internal Assurance Group
(IAG) headed by Group Director - Internal Assurance.
M/s. KPMG and M/s. ANB & Co (ANB) are the Internal
Auditors of the Company which conducts financial,
compliance and process improvement audits each year.
Our Audit Committee oversees the scope and evaluates
the overall results of these audits, and members of that
Committee regularly attend meetings of Board of Directors.
The Audit Committee also reviews the effectiveness of the
internal control system, and invites functional Directors
and senior management personnel to provide updates on
operating effectiveness and controls, from time to time.
A CEO and CFO Certificate from all operating entities,
forming part of the Corporate Governance Report, confirms
the existence and effectiveness of internal controls and
reiterates their responsibilities to report deficiencies to the
Audit Committee and rectify the same. The Company’s code
of conduct requires compliance with law and Company
policies, and also covers matters such as financial integrity,
avoiding conflicts of interest, workplace behaviour, dealings
with external parties and responsibilities to the community.
Audits are categorised into defined assurance tracks with
M/s. KPMG responsible to audit Finance and Technology
track and ANB responsible to audit Customer and L&R
track. M/s. KPMG is also engaged to perform forensics work.
Bottom-up risk assessment and directional inputs from the
Audit & Risk Management Committee formed the basis of
audit priorities. The Company was awarded for ‘Innovation
in Internal Audit 2016’ by the Institute of Internal Auditors,
India. The award recognises entities for innovation in the
use of technology, controls, business process and internal
auditing in an innovative manner for business impact.
The Airtel Centre of Excellence (‘ACE’) based in Gurgaon
and Bengaluru, is the captive shared service for Financial
Accountage, Revenue Assurance, SCM and HR processes. It
continues to expand its footprint across 20 countries thereby
ensuring standardisation of all these processes across the
organisation with inbuilt embedded controls. Digitisation of
ACE is being aimed as a part of the transformation agenda
and includes initiatives like system based reconciliation,
reporting processes with vividly defined segregation of duties.
ERP integration in Africa into an Oracle Single Instance has
been accomplished across all African countries, ensuring
uniformity and standardisation in ERP configurations, chart
of accounts, finance and SCM processes across countries.
Quality of financial reporting and controls continues to show
improvement. We continuously examine our governance
practices to enhance investor trust and improve the Board’s
overall effectiveness. Initiatives undertaken in the previous
year’s such as virtual desktop interface for ultimate data
security, self-validation checks, desktop reviews and regular
physical verification are producing measurable outcomes
through substantial improvement in control scores across
both India and Africa.
Oracle Governance Risk & Compliance (GRC) module
has been implemented for India and Africa to strengthen
existing controls pertaining to access rights for various ERPs,
ensuring segregation of duties and preventing possibilities
of access conflicts.
Material Developments in Human Resources
At Bharti Airtel, talent has always been key to our sustainable
growth. From the roll-out of 4G technology to the latest
digital apps, brilliant customer experience and new service
propositions, our people are involved in both design and
execution. We realise that our ability to continue and sustain
our growth and extraordinary success strongly depends
on our ability to grow and nurture this talent. Through our
10-point Talent First agenda, the people pillar of the Airtel
GPS, our endeavour is to provide an enabling environment
that empowers our employees to learn, grow and succeed.
In 2015-16, we encouraged a culture of performance
excellence by providing employees complete clarity on
their goals. Employees were expected to set only four KRAs,
three operational and one strategic. Mid-year and year-end
performance assessments and dialogues provided a view of
the employee’s performance to his / her reporting manager,
who in turn provided feedback to the person concerned.
Employees’ performance and potential were then discussed
in Talent Councils to enable ‘One View of Talent’ across the
Company; and ensure that leaders are made accountable
for talent development. The Company’s leadership
development strategy is focused on nurturing in-house
talent through need-based interventions. With an internal
succession rate of over 70% and over 16% of employees
with cross-functional experience, the Company has
been able to provide accelerated career and development
opportunities to its young talent.
At the senior leadership level, succession planning was
conducted for critical roles to ensure a ready pipeline. A
360-degree feedback survey was administered for over
370 senior leaders across India and Africa to enhance
leadership effectiveness. The year saw the launch of Airtel’s
new Learning Management System, iLearn, with interactive
features like social learning, virtual connect sessions,
e-libraries and so on. There was a continued focus on role-based
academies for critical talent like the Zonal Business
Manager Academy. The Company’s high impact functional
learning programmes in Sales, Marketing, Network,
Finance, SCM and IT and prestigious external leadership
development programmes, also enabled enriching learning
experiences. We also launched an induction module giving
an overview of Bharti Group, Airtel and its business verticals.
As a part of our commitment to build a diverse workforce,
we increased our Maternity leave policy from the existing
12 weeks to 22 weeks, along with the Company’s pledge
to provide the same or an equivalent role to the woman
employee on return.
The Company has also launched the Mood-o-Meter app,
which gives employees an option to provide feedback
throughout the year. With thousands of employees working in
the market, field and stores, this unique feature of feedback-on-the-go
is useful to regularly feel the organisational pulse.
The past year also saw multiple initiatives to brand Airtel as
an Employer of Choice. Some of them are: Airtel Stories
(highlighting the career journey of employees); launching a
refurbished Airtel careers website; and enhanced presence
on LinkedIn (over 238,790 followers) and Facebook.
Airtel was ranked No 1 in Business Today’s Best Companies
to Work For survey in the telecom sector, and No 8 overall. In
Africa, Airtel was awarded the Best Organisation in the L&D
category in the Café Africa 2015 eLearning International
Conference. In another prestigious recognition, an Airtel
employee in Seychelles, Ms. Erna Hoarau, was bestowed
with the National Employee of the Year award for the ICT
Industry by the Ministry of Labour & HRD.
Outlook
India’s telecommunications sector continues to be an
integral part of the country’s engine of growth, innovation
and disruption. With a subscriber base of nearly
1,058.86 Mn at the end of March 2016, India has the
world’s second largest telecom network. Mobile based
Internet is a key component of the country’s internet usage,
with seven out of eight users accessing internet from their
mobile phones. The availability of affordable smartphones
is driving industry growth. Smartphones will likely account
for over 80% of annual phone shipments by 2018. Thanks
to e-commerce, mobile banking and high quality content
viewing (anytime anywhere), India is set to witness an
exponential data growth, while voice growth is largely
stabilising.
Africa’s telecom sector has seen exponential growth in
mobile phone usage since the early 2000s. Over the
past year, digital innovation continues to transform the
continent’s economic and business landscape. There are
substantial growth opportunities in the data market in Africa,
both in terms of data connectivity and data based services.
Africa bypassed fixed lines to develop mobile networks.
Additionally, mobile money has significantly enhanced
financial inclusion in Africa. Africa’s mobile Money Market is
expected to grow nearly sevenfold by 2020.
Telecom operators continue to invest heavily on networks
to tap the increased demand from the sector. Bharti Airtel’s
pan-India 4G footprint, payments bank license, South Asian
presence, diversified product portfolio, and network rollouts
in Africa will act as a major stimulus to the Company’s growth.