Understanding RF Internet in the Modern Connectivity Era
-
September 28, 2022
-
6 min read

You have probably never thought about how your business would stay online if fibre suddenly went down. Or what if you needed to set up operations somewhere fibre or cable simply doesn’t exist? For companies working in construction sites, remote warehouses, temporary event zones, or developing regions, that’s a daily reality. This is where RF Internet earns its place.
Far from outdated, radio frequency-based connectivity still solves real problems in places where fibre can’t. In this piece, we break down what RF Internet actually is, how it works, and why it still matters in an era dominated by 5G and gigabit promises.
What is an RF Internet Connection?
RF full form is Radio Frequency, and it refers to the range of electromagnetic waves typically used for wireless transmission. In the context of internet connectivity, RF technology serves as a backbone for transmitting and receiving data wirelessly across devices, towers, and access points.
Defining RF in the Context of Wireless Communication
RF is used in multiple domains, including broadcasting, mobile communication, and satellite links. But what is RF in networking terms exactly? Simply put, it’s the medium over which wireless internet signals travel. These frequencies range from 3 kHz to 300 GHz and enable devices to communicate without needing physical cables.
When deploying an RF device for internet, service providers use RF waves to deliver the internet to homes, businesses, and remote locations. This method offers flexible deployment, especially where fibre or copper lines are unavailable.
RF Internet Vs Traditional Wired Connections
Wired connections like Ethernet rely on cables for data transfer. These offer stable performance but require substantial infrastructure. RF Internet, on the other hand, transmits data through the air, which speeds up installation and scales well across distances.
In rural or hard-to-reach areas, RF Internet becomes especially valuable. Companies that need reliable service without trenching cables often adopt an RF device in networking setups to bypass physical infrastructure limitations.
Key Features and Advantages of RF Internet
RF Internet has evolved rapidly over the past decade. Its standout features include:
- Flexibility: No need for physical lines.
- Scalability: Easy to expand coverage in growing networks.
- Quick Deployment: Infrastructure can be set up in days, not weeks.
- Low Latency: Advances in modulation and frequency tuning reduce lag.
Businesses looking to implement secure connections often evaluate RF as part of their broader digital strategy alongside options like internet leased lines.
How RF Internet Connections Work
Understanding how RF Internet functions requires a look into its core transmission and reception mechanisms.
Transmission: How Data is Sent via Radio Waves
RF Internet starts with modulation. Data is converted into a signal and modulated onto an RF carrier wave. This wave is transmitted via an antenna over a chosen frequency band.
When deploying an RF link, the signal travels from the base station to the receiver, be it a home unit or an enterprise-grade receiver, where it demodulates and converts back to digital data.
Reception: Receiving & Decoding the Signal
Once the RF wave reaches its destination, the receiver demodulates it to extract usable data. The stability of the connection depends on factors like line-of-sight, frequency interference, and antenna positioning. Today’s receivers can dynamically switch frequencies to minimize data loss and maintain consistent speeds.
This capability supports advanced services such as IoT connectivity, where constant communication between devices is essential.
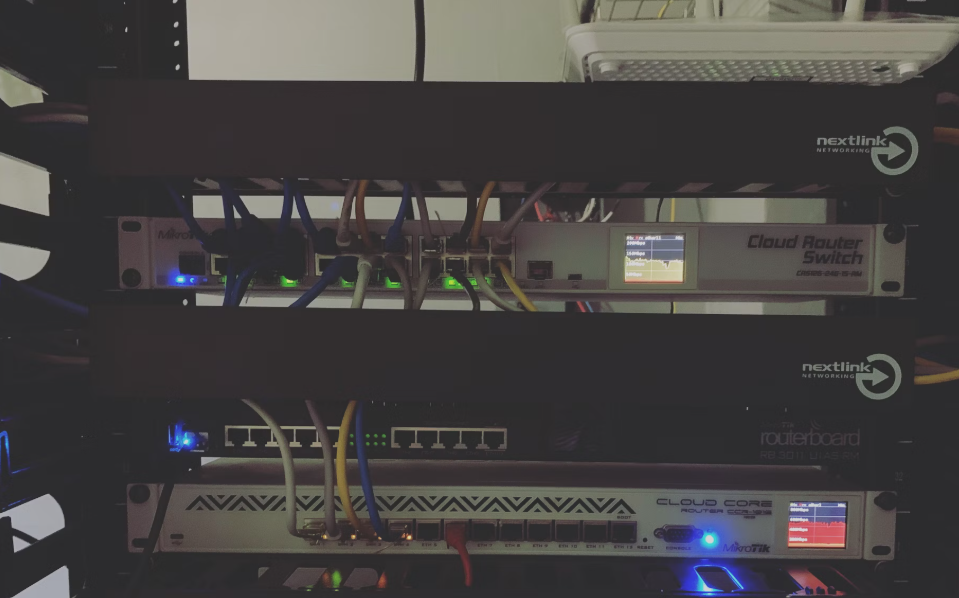
Role of Antennas, Modulators, and Repeaters
The hardware involved in RF Internet includes directional antennas, modulators for signal encoding, and repeaters that amplify signals over long distances.
Repeaters play a crucial role in extending signal range. They receive a weak signal, amplify it, and retransmit it. This keeps connections stable in large-scale networks.
How RF Powers Next-Gen Connectivity
RF technology plays a foundational role in next-generation connectivity by enabling high-speed, wireless communication without the need for physical cabling. It supports large-scale deployment of smart systems, including IoT applications, autonomous machinery, and real-time monitoring in industries like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing.
Businesses use RF to power critical operations where wired infrastructure is either impractical or too costly to install. It also supports fast-growing enterprise environments that demand flexible and responsive connectivity.
For instance, services like Airtel Office Internet can integrate RF technology to extend coverage in hard-to-wire office spaces or multi-location setups. As digital infrastructure evolves, RF continues to bring innovations in wireless connectivity and provide scalable and efficient communication for tomorrow’s connected environments.
Types of RF Connectors and Components
The hardware used in RF setups determines the quality and reliability of the network. Knowing the right components is key.
Common RF Connector Types (SMA, N-Type, BNC, etc.)
Different environments require different connectors. For example:
- SMA (SubMiniature Version A): Used in high-frequency connections in compact spaces.
- N-Type Connectors: Robust and weatherproof; used outdoors.
- BNC Connectors: Common in video and test applications.
Each serves a unique function in building a stable RF network, which is essential in both industrial and commercial contexts.
Importance of Shielding and Signal Integrity
External interference can degrade signal quality. High-end RF components use shielding to maintain signal integrity. This reduces signal reflections, cross-talk, and external noise.
Enterprises often turn to managed WiFi routers that integrate RF technologies while managing interference internally, delivering a balanced and reliable wireless experience.
Real-World Applications of RF Internet Connections
The rise of Airtel Private 5G and fibre has sparked debates about RF’s relevance, but it is still widely used across multiple sectors:
- Agriculture: Supports smart irrigation and soil monitoring through RF-based IoT networks.
- Healthcare: Enables medical telemetry and wireless patient monitoring.
- Education: Connects schools in remote areas with high-speed wireless broadband.
The integration of IoT in these environments relies heavily on RF communication. It forms the data backbone for smart devices, sensors, and edge processing units.
Benefits and Limitations of RF Internet
RF Internet offers several business advantages but also has limitations.
Benefits
- Rapid deployment in underserved areas.
- Lower infrastructure costs.
- Wide coverage without physical dependency.
Limitations
- Prone to interference from physical obstacles.
- Performance varies with weather and environmental conditions.
- Limited frequency availability due to regulatory constraints.
Despite its challenges, RF remains an integral part of modern wireless strategies. It often supports robust backup systems for primary fibre links or hybrid models.
For tech leaders, it’s important to assess use cases. Whether integrating with IoT devices or as part of a broader 5G strategy, RF offers critical wireless capabilities, especially where cables cannot go.
The Future of RF Internet in a Wireless-First World
RF internet now plays a crucial role in maintaining connectivity for businesses and communities. As the world moves toward wireless-first strategies, RF technology will play an important role in supporting IoT expansion, remote operations, and smart infrastructure.
Its ability to deliver fast, flexible connectivity makes it a go-to solution in environments where traditional cabling falls short. With advancements in frequency management and device interoperability, RF will continue to evolve with future digital demands.
For organisations seeking reliability, speed, and adaptability, solutions backed by expertise in RF networking offer a solid foundation. Whether you’re setting up from scratch or growing your network, Airtel can help you stay ahead in this digital world.
 Share
Share